Compact, low-power motor control is a common requirement in portable electronics, smart gadgets, toys, wearables, and custom embedded products. In many client projects, using a full-size Arduino is unnecessary due to size, power, and cost constraints.
This guide explains how to control a DC motor using an ATtiny85 microcontroller, a transistor, and a push button, powered entirely by a 3.7V Li-ion battery with a TP4056 charging module.
The project was developed for a client as part of our ATtiny85-Projects and Arduino Project Services, focusing on minimal hardware, low power consumption, and reliable operation. If you want to control a heating pad with ATtiny85 then Checkout Our Project Smart Heating Pad Timer Control Device Using ATtiny85

Project Overview: ATtiny85 Motor Control
This project demonstrates a standalone DC motor controller where:
- ATtiny85 acts as the main controller
- A push button is used to turn the motor ON or OFF
- A transistor works as a switching device to drive the motor safely
- A 3.7V Li-ion battery powers the entire system
- A TP4056 charging module enables safe USB charging
The design is ideal for battery-powered embedded products where efficiency and compactness are critical.
Working of ATtiny85 DC Motor Control Project
- The user presses a push button
- ATtiny85 reads the button state
- Based on the logic in the firmware:
- The motor turns ON or OFF
- The ATtiny85 controls a transistor, which switches the motor power
- The system runs from a single 3.7V battery, rechargeable via TP4056
This simple architecture ensures safe motor operation without overloading the microcontroller.
Components Used for Motor with ATtiny85
- ATtiny85 Microcontroller
- DC Motor (3–6V)
- NPN Transistor / Logic-Level MOSFET
- Push Button
- 3.7V Li-ion / Li-Po Battery
- TP4056 Charging Module
- Flyback Diode (motor protection/Optional)
- Resistors (base/gate & pull-ups)
- Connecting wires
System Power Design: 3.7V Battery & TP4056 Charging Module
Battery Power
- Single 3.7V Li-ion / Li-Po battery
- Powers both ATtiny85 and DC motor
- Ideal for portable and handheld products
TP4056 Charging Module
- Provides safe USB charging
- Includes over-charge and over-discharge protection
- Enables plug-and-play battery management
This power architecture is widely used in commercial embedded products and ATtiny85-based devices.
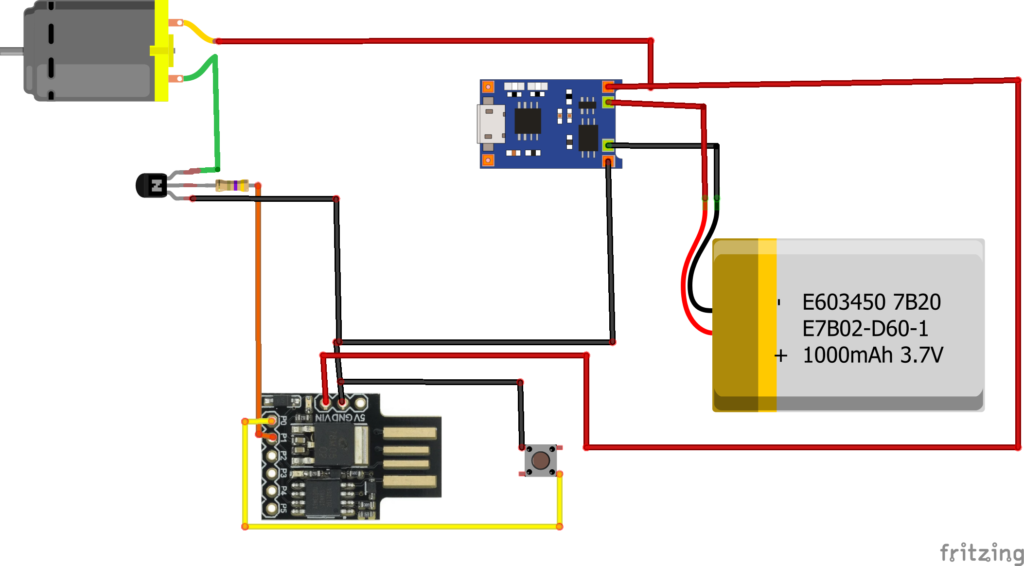
Circuit Diagram of DC Motor with ATtiny85 and Transistor and Charging Chip
Code for ATtiny85 Motor Control Project
int button=0;
int motpin=1;
bool value=false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(button,INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(motpin,OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
if(digitalRead(button)==LOW && value==false){
value=true;
Serial.println("Button Pressed");
Run_motor();
}
else if (digitalRead(button)==LOW && value==true){
value=false;
analogWrite(motpin,0);
delay(1000);
}
}
void Run_motor(){
for(int i=0;i<255;i++){
analogWrite(motpin,i);
delay(19);
}
digitalWrite(motpin,255);
}Arduino / ATtiny85 Code Explanation
The uploaded code implements a button-controlled motor switching logic optimized for ATtiny85.
1. Pin Configuration
- One GPIO pin is configured as button input
- One GPIO pin is configured as motor control output
- Internal pull-up or pull-down logic is used to simplify wiring
ATtiny85 Pinout and GPIO Configuration Guide
2. Button Input Handling
- The code continuously monitors the push button state
- Button press is detected using digital input reading
- Simple logic ensures reliable detection
This makes the system suitable for human-interface control in compact devices.
3. Motor Control Logic
- When the button is pressed:
- The ATtiny85 sets the output pin HIGH or LOW
- This output controls the base/gate of the transistor
- The transistor switches the motor power safely
The motor never connects directly to the microcontroller, which is critical in professional embedded design.
4. Transistor-Based Switching
- The transistor acts as an electronic switch
- ATtiny85 provides only a small control signal
- The transistor handles the motor current
This approach:
- Protects the ATtiny85
- Enables higher motor current
- Improves system reliability
5. Stable Loop Execution
- The loop runs continuously
- Motor state updates immediately based on button input
- Optional small delays ensure stable operation
This ensures responsive motor control, even with limited ATtiny85 resources.
Applications of This ATtiny85 DC Motor Control Project
- Battery-powered toys
- Portable fans or pumps
- Smart locks and actuators
- DIY gadgets
- Educational ATtiny85 projects
- Compact automation modules
- Client-specific embedded products
Possible Enhancements
- PWM speed control
- Long-press / short-press logic
- Sleep mode for ultra-low power
- Direction control using H-bridge
- Wireless control (BLE module)
- Status LED indication
Conclusion
The DC Motor Control Using ATtiny85, Transistor, and Push Button project is a compact yet powerful example of modern embedded system design. Powered by a 3.7V battery and TP4056 charger, it is perfectly suited for portable and commercial applications.
Developed as a client project, this guide highlights our expertise in ATtiny85-Projects and Arduino Project Services, delivering efficient, reliable, and production-ready solutions.
If you need Help in ATtiny85 DC Motor Control Project with or without Modifications or Customization then you can contact us through WhatsApp. Learn More about the Services we offer.



